Posterior Wall Myocardial Infarction Is Best Identified in Which Leads
In this setting ST-segment depressions appear in the right precordial leads V1 V2 and V3 along with classic ST-segment elevations in the inferior leads. In isolated posterior wall occlusion MI a standard 12-lead ECG will not be able to capture any ST-segment elevation and manifests as ST depression instead in leads V1-V4 While it is important to know the STEMI criteria and that posterior leads can be used to diagnose OMI posterior leads may be falsely negative and the STEMI criteria is unacceptably insensitive for OMI and.

Posterior Myocardial Infarction How Accurate Is The Flipped Ecg Trick
A posterior wall myocardial infarction is best identified in which leads.
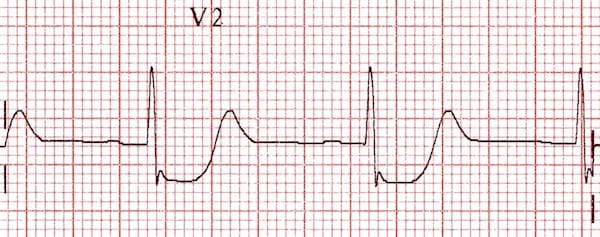
. ST-segment elevation 05 mm in posterior leads V8 and V9 is sensitive for posterior wall infarction 8 as high as 90 with predictive accuracy up to 938 47. Posterior myocardial infarction MI represents 33 21 of all acute MIs and can be difficult to diagnose by the standard precordial leads. Limited data exist on the prevalence and prognosis of isolated posterior ST-segment elevation acute myocardial infarction STEMI revealed with a posterior chest lead.
However electrocardiography using right side V2R-V4R and posterior V7-9 chest leads lower panel showed pathologic Q waves in posteriot chest leads. 1 and aVL D. RVMI can occur with or without LV.
Luckily leads V1 V3 directly face the posterior wall of the left ventricle and are the mirror image of the posterior wall of the left ventricle. An acute myocardial infarction causes a number of electrocardiogram ECG changes corresponding to coronary anatomy. ST segment depression not elevation in the septal and anterior precordial leads V1.
However isolated posterior MI while less common 3-11 of infarcts 2 is important to recognize as it is also an indication for reperfusion and can be missed by the ECG reader. Posterior wall ST-elevation myocardial infarction commonly occurs as a complication or extension of acute inferior wall STEMI. Recent reports have demonstrated that artificial neural networks can be used to.
Up to 10 cash back Abstract. This activity will discuss the pertinent topics related to the pathophysiology diagnosis and treatment of right ventricular myocardial infarction RVMI. The arrow points to a.
Automated interpretation of ECG is widely used as decision support for less experienced physicians. Posterior wall MI is most commonly associated with an inferior or lateral STEMI occurring 15-20 percent of the time. Typically leads V7 V9 are needed to diagnose this entity.
In most patients the inferior myocardium is supplied by the right coronary artery. V1 and V2 C. The precordial ST-segment depressions are the mirror image of ST.
Development of pathologic Q waves in leads I aV L V 5 and V 6. Inferior infarction is determined by ECG changes such as ST segment elevation T wave inversion and the development of pathologic Q waves in Leads II III and aV F. Unless there is timely treatment this results in myocardial ischemia followed by infarction.
Furthermore the utility of a synthesized-V 79 lead in the diagnosis of STEMI is unclear. Therefore we aimed to evaluate its usefulness. The addition of posterior leads V 7 to V 9 significantly increases the ability to detect posterior injury patterns compared with the standard 12-lead ECG.
RVMI was first identified in patients with inferior wall MI who had elevated right ventricular RV filling pressures and RV failure with normal values for the left ventricle LV. 5 Various abnormalities of the R wave in leads V1 or V2 are reported to be other major electrocardiographic features associated with posterior wall myocardial infarction. Posterior infarction is diagnosed based on the presence of ST segment elevation 05mm in leads V7-9.
12 The posterior myocardial infarction PMI refers to an infarction of the posterior wall of the left ventricle LV. Posterior infarctions can be diagnosed by looking for reciprocal changes in leads V 1 and V 2. ST-Segment Depressions in Precordial Leads V1V3 Indicating Posterior or Posterolateral Wall STEMI.
V4 and V5 B. While transmural infarction the result of STEMI or OMI of other walls registers as positive or elevated changes on the corresponding leads of the standard 12 leads eg inferior STEMI has ST elevations in the inferior leads II III and aVF posterior MI registers only reciprocal changes on the standard anterior leads because there is no standard lead overlying the. At 3 days there is a zone of yellow necrosis surrounded by darker hyperemic borders.
A combination of horizontal ST segment depression with tall upright T waves in the right precordial leads is highly suggestive of acute posterior wall myocardial infarction. The ECG findings of an acute posterior wall MI include the following. Background The 12-lead ECG together with patient history and clinical findings remains the most important method for early diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction.
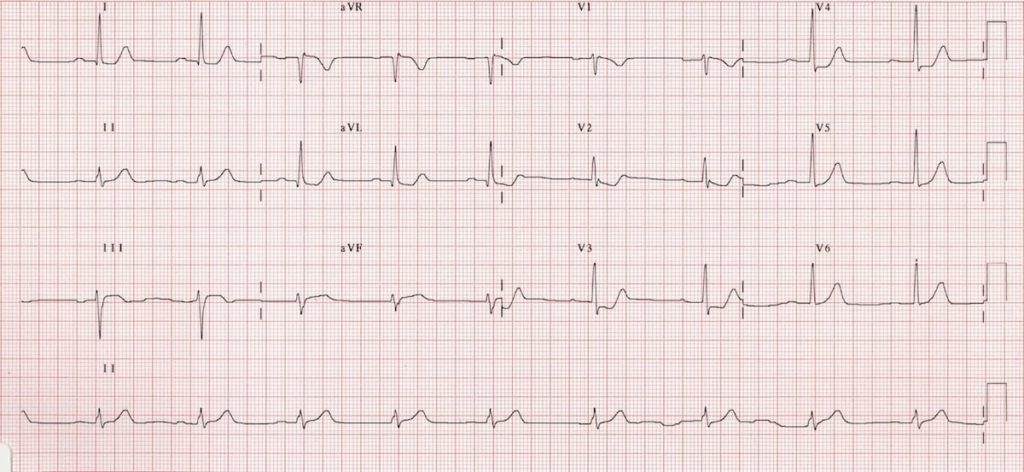
3 On the 12-lead ECG the key to detecting a PMI is through indirect evidence via ST-depression in the antero-septal V1V4 leads and. Inferior wall myocardial infarction MI occurs from a coronary artery occlusion with resultant decreased perfusion to that region of the myocardium. Note that there is also some inferior STE in leads III and aVF but no Q wave formation suggesting early inferior involvement.
As discussed in Chapter 4 these patients must not be classified as having a non-STEMI or just anterior wall ischemia ST-segment depressions in the right precordial leads V1V3 accompanied by upright T-waves makes an acute posterior wall. Acute myocardial infarct. An ECG performed with the use of posterior leads revealed ST-segment elevation in leads V 7 V 8 and V 9 which was consistent with posterior-wall myocardial infarction.
57 Lead V 7 should be placed at the level of lead V 6 at the posterior axillary line lead V 8 on the left side of the back at the tip of the scapula and lead V 9 halfway between lead V 8 and the left paraspinal muscles.

No comments for "Posterior Wall Myocardial Infarction Is Best Identified in Which Leads"
Post a Comment